Porter's Five Forces
Simple but powerful tool for understanding where power lies in a business situation
The Porter's Five forces model of pure competition implies that risk-adjusted rates of return should be constant across firms and industries. However, numerous economic studies have affirmed that different industries can sustain different levels of profitability; part of this difference is explained by industry structure.
Michael Porter provided a framework that models an industry as being influenced by five forces. The strategic business manager seeking to develop an edge over rival firms can use this model to better understand the industry context in which the firm operates.
The Porter's Five Forces tool is a simple but powerful tool for understanding where power lies in a business situation. This is useful, because it helps you understand both the strength of your current competitive position, and the strength of a position you're considering moving into.
With a clear understanding of where power lies, you can take fair advantage of a situation of strength, improve a situation of weakness, and avoid taking wrong steps. This makes it an important part of your planning toolkit.
Conventionally, the tool is used to identify whether new products, services or businesses have the potential to be profitable. However it can be very illuminating when used to understand the balance of power in other situations.
-
Buying power of customers
-
Size of each order
-
Differences between competitors
-
Price sensitivity
-
Ability to substitute
-
Cost of changing
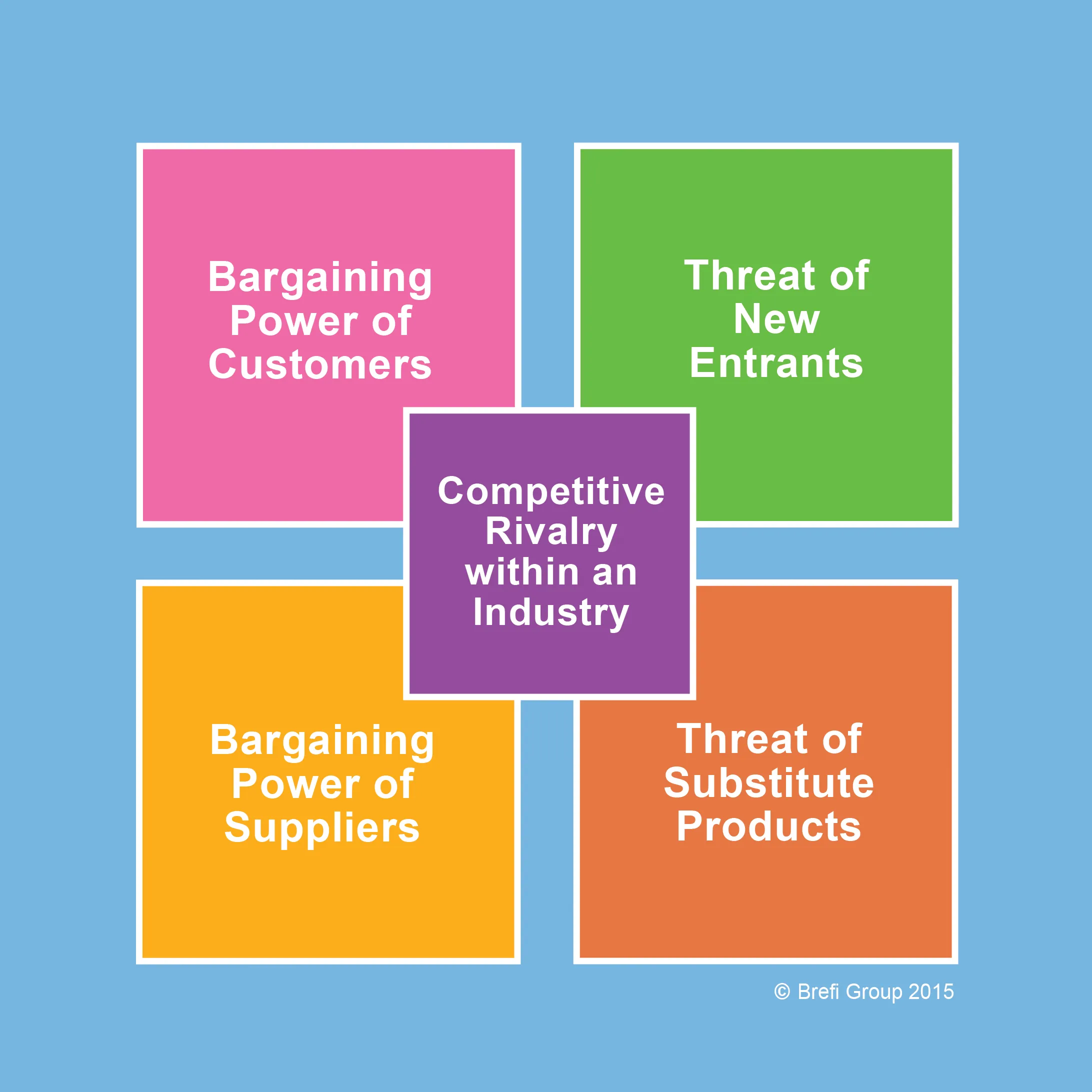
Bargaining power of customers affects how easy it is for buyers to drive prices down.
-
Number of suppliers
-
Size of suppliers
-
Uniqueness of service
-
Your ability to substitute
-
Cost of changing
Bargaining power of customers affects how easy it is for buyers to drive prices down.Bargaining power of suppliers affects how easy it is for suppliers to drive up prices.
-
Time and cost of entry
-
Specialist knowledge
-
Economies of scale
-
Cost advantages
-
Technology protection
-
Barriers to entry
Threat of new entrants is affected by the ability of people to enter your market.
-
Substitute performance
-
Cost of change
Threat of substitute products is affected by the ability of your customers to find a different way of doing what you do.
-
Number of competitors
-
Quality of differences
-
Other differences
-
Switching costs
-
Customer loyalty
Competitive rivalry within your industry depends on the number and capability of your competitors.
With a clear understanding of where power lies, you can take fair advantage of a situation of strength, improve a situation of weakness and avoid taking wrong steps. This makes it an important part of your planning toolkit.
Conventionally, the tool is used to identify whether new products, services or businesses have the potential to be profitable. However it can be very illuminating when used to understand the balance of power in other situations.
Brefi Group Limited
Unit 11 BSC, Hood Road
Barry CF62 5QN
United Kingdom
Reg. No. 1669333
Copyright 2024 Brefi Group Limited. All Rights Reserved
