What If and Why-Why Diagrams
What-iffing is a form of brainstorming
What-iffing is a form of brainstorming. Raise a number of possibilities, including those that seem to be totally unlikely or impossible and answer the question “What if…. ?”
A Why-Why Diagram is a Tree Diagram where each child statement is determined simply by asking 'why' the parent occurs, as below. It is thus very similar in use to a Cause-Effect Diagram, and techniques may be borrowed from Cause-Effect Diagram usage. Its simplicity can make it useful in less formal situations.
Why-Why diagrams enable individuals and groups to creatively explore and consider numerous causes of a problem (or needs for an opportunity). They help individuals achieve divergent thinking.
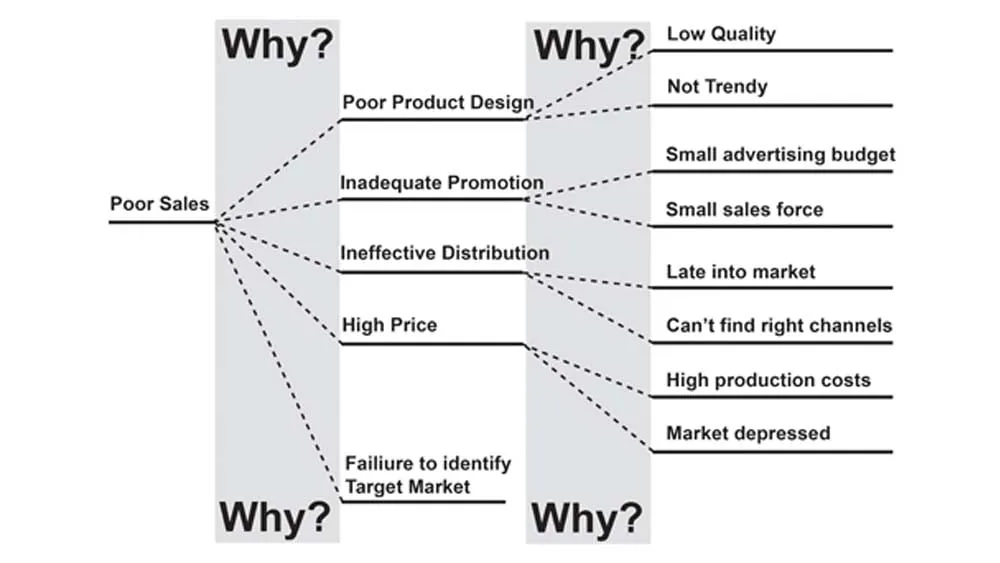
Why diagrams trace the reasons for a problem.
-
They allow you to get to the root cause of a problem.
-
They allow a group of people to share a problem or situation and hence work together to solve it.
-
They allow you to consciously not follow some paths, digging only into the most likely areas.
-
Develop a problem statement or focus
-
Explore possible causes of the problem (or reasons for addressing an opportunity) by asking “Why?”
-
For each possible cause (or reason) again explore possible causes for this lower level problem by asking “Why? (the answers to the questions “Why” are the causes of the problem)
The steps of a Why-Why diagram:
Brefi Group Limited
Unit 11 BSC, Hood Road
Barry CF62 5QN
United Kingdom
Reg. No. 1669333
Copyright 2024 Brefi Group Limited. All Rights Reserved
